标签:Paths right TreeNode val Binary int Tree path root
Given a binary tree where node values are digits from 1 to 9. A path in the binary tree is said to be pseudo-palindromic if at least one permutation of the node values in the path is a palindrome.
Return the number of pseudo-palindromic paths going from the root node to leaf nodes.
Example 1:
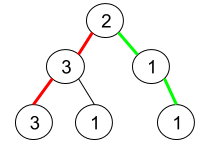
Input: root = [2,3,1,3,1,null,1] Output: 2 Explanation: The figure above represents the given binary tree. There are three paths going from the root node to leaf nodes: the red path [2,3,3], the green path [2,1,1], and the path [2,3,1]. Among these paths only red path and green path are pseudo-palindromic paths since the red path [2,3,3] can be rearranged in [3,2,3] (palindrome) and the green path [2,1,1] can be rearranged in [1,2,1] (palindrome).
Example 2:
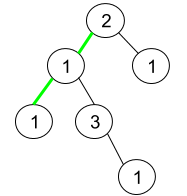
Input: root = [2,1,1,1,3,null,null,null,null,null,1] Output: 1 Explanation: The figure above represents the given binary tree. There are three paths going from the root node to leaf nodes: the green path [2,1,1], the path [2,1,3,1], and the path [2,1]. Among these paths only the green path is pseudo-palindromic since [2,1,1] can be rearranged in [1,2,1] (palindrome).
Example 3:
Input: root = [9] Output: 1
Constraints:
- The given binary tree will have between
1and10^5nodes. - Node values are digits from
1to9.
二叉树中的伪回文路径。
给你一棵二叉树,每个节点的值为 1 到 9 。我们称二叉树中的一条路径是 「伪回文」的,当它满足:路径经过的所有节点值的排列中,存在一个回文序列。
请你返回从根到叶子节点的所有路径中 伪回文 路径的数目。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/pseudo-palindromic-paths-in-a-binary-tree
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路是DFS + 回溯。这道题跟113题很像,你需要去找到树中每一条从根节点到叶子节点的路径,然后再多一步判断,判断每一条路径是不是满足题目定义的伪回文。判断伪回文额外写一个函数判断即可。这里我提供两种做法,思路差不多,第一种方法速度快一些,第二种方法不使用全局变量。两种做法的时间空间复杂度均为O(n)。
DFS + 回溯
count是全局变量而且hashmap是被带入helper函数往下一层去递归的,所以需要回溯
Java实现
1 /**
2 * Definition for a binary tree node.
3 * public class TreeNode {
4 * int val;
5 * TreeNode left;
6 * TreeNode right;
7 * TreeNode() {}
8 * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
9 * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
10 * this.val = val;
11 * this.left = left;
12 * this.right = right;
13 * }
14 * }
15 */
16 class Solution {
17 int count = 0;
18
19 public int pseudoPalindromicPaths(TreeNode root) {
20 int[] map = new int[10];
21 helper(root, map);
22 return count;
23 }
24
25 private void helper(TreeNode root, int[] map) {
26 // base case
27 if (root == null) {
28 return;
29 }
30 map[root.val]++;
31 if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
32 if (isPalindrome(map)) {
33 count++;
34 }
35 }
36
37 helper(root.left, map);
38 helper(root.right, map);
39 map[root.val]--;
40 }
41
42 private boolean isPalindrome(int[] map) {
43 int single = 0;
44 for (int i = 0; i < map.length; i++) {
45 if (map[i] % 2 == 1) {
46 single++;
47 }
48 }
49 return single > 1 ? false : true;
50 }
51 }
更像前序遍历的一种做法,没有回溯
Java实现
1 /**
2 * Definition for a binary tree node.
3 * public class TreeNode {
4 * int val;
5 * TreeNode left;
6 * TreeNode right;
7 * TreeNode() {}
8 * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
9 * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
10 * this.val = val;
11 * this.left = left;
12 * this.right = right;
13 * }
14 * }
15 */
16 class Solution {
17 public int pseudoPalindromicPaths(TreeNode root) {
18 return helper(root, new HashSet<>());
19 }
20
21 private int helper(TreeNode root, HashSet<Integer> set) {
22 if (root == null) {
23 return 0;
24 }
25 if (set.contains(root.val)) {
26 set.remove(root.val);
27 } else {
28 set.add(root.val);
29 }
30 if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
31 return set.size() <= 1 ? 1 : 0;
32 }
33 // 注意这里hashset的细节
34 int left = helper(root.left, new HashSet<>(set));
35 int right = helper(root.right, new HashSet<>(set));
36 return left + right;
37 }
38 }
相关题目
1457. Pseudo-Palindromic Paths in a Binary Tree
标签:Paths,right,TreeNode,val,Binary,int,Tree,path,root 来源: https://www.cnblogs.com/cnoodle/p/14209563.html
本站声明: 1. iCode9 技术分享网(下文简称本站)提供的所有内容,仅供技术学习、探讨和分享; 2. 关于本站的所有留言、评论、转载及引用,纯属内容发起人的个人观点,与本站观点和立场无关; 3. 关于本站的所有言论和文字,纯属内容发起人的个人观点,与本站观点和立场无关; 4. 本站文章均是网友提供,不完全保证技术分享内容的完整性、准确性、时效性、风险性和版权归属;如您发现该文章侵犯了您的权益,可联系我们第一时间进行删除; 5. 本站为非盈利性的个人网站,所有内容不会用来进行牟利,也不会利用任何形式的广告来间接获益,纯粹是为了广大技术爱好者提供技术内容和技术思想的分享性交流网站。
