标签:binary sequence int Rebuild tree traversal 二叉树 Proper now
真二叉树重构(Proper Rebuild)
Description
In general, given the preorder traversal sequence and postorder traversal sequence of a binary tree, we cannot determine the binary tree.
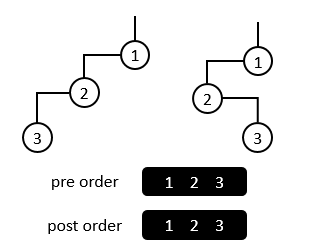
Figure 1
In Figure 1 for example, although they are two different binary tree, their preorder traversal sequence and postorder traversal sequence are both of the same.
But for one proper binary tree, in which each internal node has two sons, we can uniquely determine it through its given preorder traversal sequence and postorder traversal sequence.
Label n nodes in one binary tree using the integers in [1, n], we would like to output the inorder traversal sequence of a binary tree through its preorder and postorder traversal sequence.
Input
The 1st line is an integer n, i.e., the number of nodes in one given binary tree,
The 2nd and 3rd lines are the given preorder and postorder traversal sequence respectively.
Output
The inorder traversal sequence of the given binary tree in one line.
Example
Input
5
1 2 4 5 3
4 5 2 3 1Output
4 2 5 1 3Restrictions
For 95% of the estimation, 1 <= n <= 1,000,00
For 100% of the estimation, 1 <= n <= 4,000,000
The input sequence is a permutation of {1,2...n}, corresponding to a legal binary tree.
Time: 2 sec
Memory: 256 MB
Hints
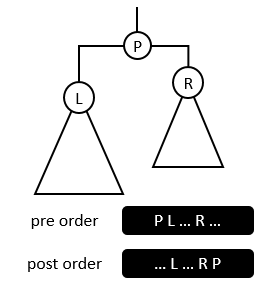
Figure 2
In Figure 2, observe the positions of the left and right children in preorder and postorder traversal sequence.
- 原理与要点:利用树的先序与后序的规律,递归建树,然后dfs输出树的中序遍历。可以发现先序的第一个节点是根节点,后序的最后一个节点是根节点,利用这个规律确定左右子树,一直递归下去,就可以确定每一个节点
- 遇到的问题:无
- 时间和空间复杂度:时间复杂度\(O(nlogn)\),空间复杂度\(O(n)\)
#include <cstdlib>
#include "cstdio"
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 4e6 + 100;
const int SZ = 1 << 20; //快速io
struct fastio {
char inbuf[SZ];
char outbuf[SZ];
fastio() {
setvbuf(stdin, inbuf, _IOFBF, SZ);
setvbuf(stdout, outbuf, _IOFBF, SZ);
}
} io;
typedef struct node {
int val;
node *l, *r;
} *tree;
tree root = NULL;
int mlr[maxn], lrm[maxn];
int n;
void build(tree &t, int s1, int e1, int s2, int e2) {
t = (tree) malloc(sizeof(node));
t->val = mlr[s1];
if (s1 == e1) return;
int now;
for (int i = s2; i <= e2; i++) {
if (mlr[s1 + 1] == lrm[i]) {
now = i;
break;
}
}
build(t->l, s1 + 1, now - s2 + 1 + s1, s2, now);
build(t->r, now - s2 + 2 + s1, e1, now + 1, e2 - 1);
}
void dfs(tree now) {
if (now == NULL) return;
dfs(now->l);
printf("%d ", now->val);
dfs(now->r);
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &mlr[i]);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &lrm[i]);
}
build(root, 1, n, 1, n);
dfs(root);
return 0;
}标签:binary,sequence,int,Rebuild,tree,traversal,二叉树,Proper,now 来源: https://www.cnblogs.com/albert-biu/p/11542123.html
本站声明: 1. iCode9 技术分享网(下文简称本站)提供的所有内容,仅供技术学习、探讨和分享; 2. 关于本站的所有留言、评论、转载及引用,纯属内容发起人的个人观点,与本站观点和立场无关; 3. 关于本站的所有言论和文字,纯属内容发起人的个人观点,与本站观点和立场无关; 4. 本站文章均是网友提供,不完全保证技术分享内容的完整性、准确性、时效性、风险性和版权归属;如您发现该文章侵犯了您的权益,可联系我们第一时间进行删除; 5. 本站为非盈利性的个人网站,所有内容不会用来进行牟利,也不会利用任何形式的广告来间接获益,纯粹是为了广大技术爱好者提供技术内容和技术思想的分享性交流网站。
